Smart airbags are an advanced version of standard airbags. They use sensors to detect the size and position of passengers. They also detect their seatbelt status and the severity of the collision.
What Will I learn
In this article, we will know the mechanism and types of smart airbags. Moreover, we will learn how to maintain and replace them in the future.
Smart Airbags – Working Mechanism
Smart airbags are designed to be more effective and efficient than traditional airbags.
They use sensors and other components to trigger deployment and inflate to minimize the risk of injury to passengers.

In this section, we will discuss the working mechanism of smart airbags in detail:
Sensors And Components:
Smart airbags use accelerometers, gyroscopes, pressure sensors, and weight sensors. They detect and assess the severity of an impact.
These sensors work together to determine passengers’ size, weight, and position. They also determine whether they are wearing seatbelts.
This information helps the airbag control unit determine the appropriate level of airbag deployment.
The control unit also takes into account the vehicle’s speed and angle of impact. Thus, they ensure that the airbag deploys at the right time and with the appropriate force.
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how sensors and components work in a smart airbag system:
1. Accelerometers:
These sensors detect changes in the velocity and direction of the vehicle during a collision.
They provide information on the speed and angle of impact to the airbag control unit.
2. Gyroscopes:
Gyroscopes work with accelerometers to detect the orientation of the vehicle.
They provide information on the direction of impact and the position of the passengers.
3. Pressure Sensors:
Pressure sensors detect changes in air pressure in the vehicle’s cabin. They help the airbag control unit determine the severity of the impact.
They can also help determine the force required to deploy the airbag.
4. Weight Sensors:
Weight sensors detect the weight of the passengers and determine their position in the vehicle.
This information is crucial in determining the appropriate level of airbag deployment.
5. Airbag Control Unit:
The airbag control unit is the brain of the smart airbag system. It receives input from the sensors.
Once received, they use the inputs to analyze the data to determine when to deploy the airbag.
6. Inflator:
The inflator is responsible for deploying the airbag. It receives a signal from the airbag control unit.
The signal ignites a small amount of solid fuel, producing gas that inflates the airbag.
7. Airbag:
The airbag is the cushioning device deployed toward the passenger at high speed.
It helps reduce the impact of the collision and minimize the risk of injury to the passengers.
8. Inflation Process:
The inflation process of a smart airbag is similar to that of standard airbags. The airbag control unit sends a signal to the inflator, which ignites a small amount of solid fuel.
The propellant burns rapidly, producing a large hot gas, and inflating the airbag. This process takes only a few milliseconds.
The airbag fills with gas and deploys toward the passenger at high speed. The cushioning effect of the airbag reduces the impact of the collision. This minimizes the risk of injury to the passengers.
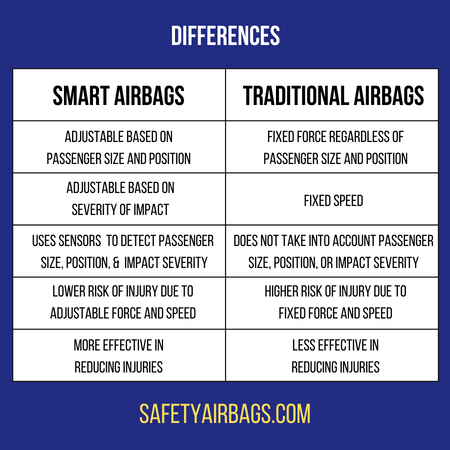
Difference From Traditional Airbags:
The primary difference between smart airbags and standard airbags is their deployment mechanism:
Types Of Smart Airbags
There are three main types of smart airbags. In this section, we will provide an overview of each type. We will also compare their working mechanisms and effectiveness.
1. Occupant-Sensitive Airbags:
Occupant-sensitive airbags use sensors to detect the size and position of passengers in the vehicle. They adjust the deployment force and speed of the airbag.
They do so based on this information to provide better protection to passengers. These airbags can also detect whether a passenger is wearing a seatbelt.
This way, they adjust the deployment force and speed accordingly.
Effectiveness:
Occupant-sensitive airbags are more effective than traditional airbags in reducing injuries.
They adjust the deployment force and speed based on the size and position of the passenger.
2. Weight-Sensitive Airbags:
Weight-sensitive airbags use sensors to detect the weight of the passengers in the vehicle.
They adjust the deployment force and speed of the airbag based on the passenger’s weight to provide better protection.
These airbags can also detect whether a passenger is carrying heavy objects. They adjust the deployment force and speed accordingly.
Effectiveness:
Weight-sensitive airbags are effective in reducing injuries. They adjust the deployment force and speed based on the passenger’s weight.
However, they may sometimes be less effective than occupant-sensitive airbags. This is because they do not consider the passenger’s position.
3. Position-Sensitive Airbags:
Position-sensitive airbags use sensors to detect the passenger’s position in the vehicle.
They adjust the deployment force and speed of the airbag based on the passenger’s position to provide better protection.

These airbags can also detect whether a passenger is too close to the steering wheel. This way, they adjust the deployment force and speed accordingly.
Effectiveness:
Position-sensitive airbags are effective in reducing injuries. This is because they adjust the deployment force and speed based on the passenger’s position.
However, they may sometimes be less effective than occupant-sensitive airbags. This is because they do not take into account the size and weight of the passenger.
Safety Benefits Of Smart Airbags
Smart airbags have been proven to provide significant safety benefits in vehicle collisions:
Statistics And Research:
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA):
Frontal airbags alone saved over 50,000 lives between 1987 and 2017 in the United States.
Additionally, studies have shown that vehicles equipped with smart airbags have a lower rate of fatalities and injuries.
Types Of Injuries:
Smart airbags prevent head, neck, and chest injuries most effectively. But, unfortunately, these are some of vehicle collisions’ most common and serious injuries.

Occupant-sensitive airbags are particularly effective in preventing injuries to children and small adults. However, they are at a higher risk of injury due to the force of standard airbags.
1. Head and Facial Injuries:
The head and facial injuries that may be at risk are:
– Concussions
– Skull fractures
– Facial lacerations
2. Eye Injuries:
Eye injuries may occur too, such as:
– Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs)
3. Neck Injuries:
Many neck injuries may happen:
– Whiplash
– Cervical fractures
– Spinal cord injuries (SCI)
4. Chest Injuries:
Chest injuries that are at risk are:
– Rib fractures
– Lung contusions
– Heart injuries
– Abdominal injuries
– Extremity Injuries:
– Arm and hand injuries
– Leg and foot injuries
– Fractures and dislocations
Other Safety Features:
Smart airbags work with other safety features to provide maximum protection to passengers.
Here’s an explanation of how smart airbags work in conjunction with other safety features to provide maximum protection:
1. Seat Belts:
Seat belts are the primary restraint system in a vehicle. They work in tandem with smart airbags to reduce the risk of injury.
The seat belt prevents the occupant from moving forward when a collision occurs. Thus, it collides with the dashboard or steering wheel.
The smart airbag then deploys to cushion the impact and provide additional protection to the occupant.
2. Pre-Collision Systems:
Pre-collision systems use sensors to detect potential collisions. Then, they prepare the vehicle’s safety systems, including smart airbags, to deploy in the event of an impact.

The pre-collision system activates the smart airbag and other safety systems when a collision is imminent. As a result, they provide maximum protection to the vehicle’s occupants.
3. Crash Sensors:
Smart airbags rely on crash sensors to detect the severity of a collision—this way, they determine whether or not to deploy.
These sensors measure the rate of deceleration and the direction of the impact. Thus, they determine the appropriate deployment force and timing.
This information is relayed to the airbag control module. In return, it activates the airbag and initiates the inflation process.
4. Occupant Detection Systems:
Occupant detection systems are used in some smart airbags. They determine whether or not an airbag should be deployed based on the weight and position of the occupant.
These systems can prevent airbags from deploying unnecessarily in a collision. Thus, they reduce the risk of injury to the occupant.
Smart airbags work in conjunction with these other safety features. Thus, they can provide maximum protection to vehicle occupants during a collision.
Limitations And Concerns
Although there are enough safety benefits of smart airbags, however, there are certain limitations; let’s discuss them in detail:
1. Side-impact collisions:
Smart airbags may not be as effective in side-impact collisions.
The impact forces are different here, and the airbags may not deploy in time to prevent injury.
2. Rear-End Collisions:
Similarly, smart airbags may not be as effective in rear-end collisions.
Here the forces involved are typically lower than in front-end collisions.
3. Multiple Impacts:
In some cases, a collision may involve multiple impacts.
It can make it difficult for smart airbags to deploy in time to provide adequate protection.
4. Occupant Position:
While some smart airbags are position-sensitive, they can adjust their deployment force based on the occupant’s position.
Thus, they may not be as effective for occupants not seated in a specific position. These may be children or adults who are lying down.
5. Vehicle Speed:
Smart airbags may not be effective at high speeds. Here the impact forces are greater.
Thus, the airbags may not deploy in time to provide adequate protection.
6. Vehicle Type:
Smart airbags may not be effective in all types of vehicles. For instance, smaller or lighter vehicles.
Vehicles that are more prone to rollovers or other types of collisions may not support these.
7. Weather Conditions:
Sometimes, weather conditions like heavy rain or snow can interfere with the sensors.
They can trigger smart airbag deployment, making them less effective.
8. Sensor Malfunction:
Like any technology, smart airbags can malfunction due to sensor failure or other technical issues.
Thus, they can prevent them from deploying or cause them to deploy unnecessarily.
9. Improper installation:
If a smart airbag is not installed properly, it may not function as intended.
It could increase the risk of injury in a collision. Moreover, it can prevent the airbag from deploying at the right time.
10. User error:
Finally, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of smart airbags also depends on user behavior.
For example, it is failing to wear a seatbelt. It sreduces the effectiveness of smart airbags and increases the risk of collision injury.
Maintenance And Replacement
Regular maintenance and inspection of smart airbags are crucial. This helps in ensuring they function properly in the event of a collision.
This includes checking the airbag warning light on the dashboard. It also includes inspecting the airbag system for damage or wear and tear.
It’s recommended to have this inspection done by a qualified mechanic or dealership.

Smart airbags have a recommended replacement interval of 10-15 years. This depends on the make and model of the vehicle.
This is because the chemicals used to inflate the airbag can break down over time. Thus, they can reduce their effectiveness in a collision.
It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for replacement. Then, they can ensure the airbags function properly in an emergency.
Replacing a smart airbag can be a complicated and expensive process. So here it is simplified in a few steps for you:
1. Disconnect The Battery:
Before starting any work on the airbag system, it’s important to disconnect the vehicle’s battery.
This can prevent accidental deployment of the airbag. However, without disconnecting, there can be a risk of injuries.
2. Remove The Old Airbag:
Depending on the make and model of the vehicle, the airbag may be located on the steering wheel, dashboard, or other locations.
The old airbag must be removed and disconnected from the electrical and airlines.
3. Install The New Airbag:
Once the old airbag has been removed, the new airbag can be installed in its place.
This involves reconnecting the electrical and airlines and any other airbag system components.
4. Test The New Airbag:
After installation, the new airbag must be tested. It should be ensured that it will function properly in a collision.
This involves a series of diagnostic tests to confirm that the airbag system is functioning correctly.
5. Reconnect The Battery:
Once the airbag system has been tested to function properly, the vehicle’s battery can be reconnected.
Reconnect the battery properly, and it is better to take help from an expert.
Cost Of Airbag Replacement:
The replacement cost can vary widely depending on the make and model of the vehicle.
It also depends on the location and availability of replacement parts. In some cases, a replacement can cost several thousand dollars.
This is specifically if the airbag system is integrated with other safety features in the vehicle. Again, it’s important to consult with a qualified mechanic or dealership.
They can accurately estimate the cost of replacing a smart airbag.
Future Developments
Smart airbag technology is an important safety feature in modern automobiles. Ongoing research and development efforts aim to improve its effectiveness.
1. One trend is using advanced sensors to better detect and respond to crash scenarios.
2. One area of research is developing airbags that can sense the position and size of passengers in the vehicle.
This is particularly important in vehicles with multiple seating positions. Different-sized occupants may require different airbag deployment strategies to prevent injury.
Some new airbag systems use pressure sensors in the seats. They determine whether a passenger is in the seat and adjust airbag deployment accordingly.
3. Another area of research is improving the responsiveness of airbags. Standard airbags are designed to deploy at a specific velocity threshold.
But this can lead to injuries if the vehicle travels faster. As a result, new airbag systems are being developed that use advanced sensors. These may be radar or LIDAR.
They detect the speed and severity of a collision and adjust airbag deployment accordingly.
4. Besides sensor technology, new materials are also being developed to improve airbag performance.
For example, some airbag manufacturers are experimenting with using carbon fiber-reinforced materials. They are lightweight and strong. Thus, they reduce the weight of airbags while still maintaining their effectiveness.
5. Another emerging trend is the use of adaptive airbags. They can adjust their shape and size to protect passengers in different crash scenarios better.
For example, some airbags can deploy in a “V” shape to better protect occupants in a side-impact crash.
Conclusion:
Smart airbags play a crucial role in promoting vehicle safety. They reduce the risk of injury or death in the event of a crash.
The development and implementation of smart airbag technology have improved the performance of airbags. This allows them to better detect and respond to crash scenarios.
They protect passengers of different sizes and positions. Thus, they reduce the risk of injury in high-speed collisions.
In conclusion, smart airbags are a critical component of modern vehicle safety.
